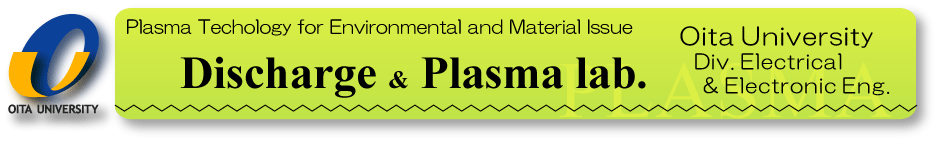
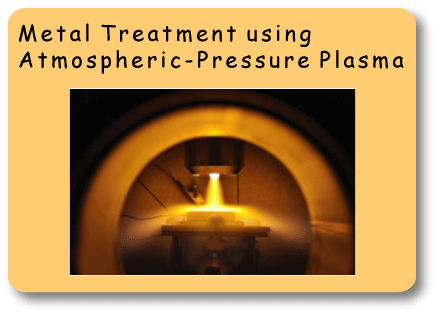
        In general, low-pressure plasmas are used for surface treatment of metals.
Our trial is to harden steel surfaces and to synthesize metal nitride layer
by using atmospheric-pressure plasmas. Here we do not need vacuum systems and the treatment takes a very short
time. Moreover, atmospheric-pressure plasma is good at partial treatment, where we can treat only desirable parts of dies and mechanical parts.
Plasma Nitriding of Steels under Atmospheric Pressure
Nitriding is a case-hardening technique to upgrade the performance of dies
and mechanical components. We are developing plasma nitriding with an atmospheric-pressure
plasma jet. This method can easily increase the surface hardness of steels
without vacuum systems and external heaters.
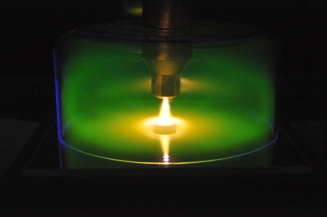 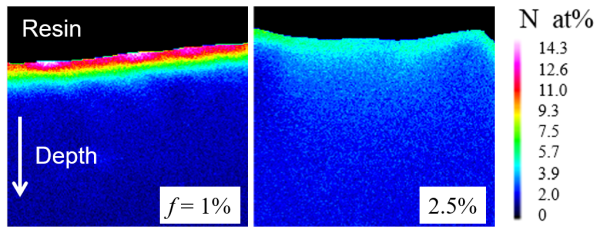 Treatment system and nitrogen mapping of nitrided steel surface ○Bright nitriding using atmospheric-pressure pulsed-arc plasma jet based on NH emission characteristics K. Toda, R. Ichiki, Y. Kanbara, K. Kojima, K. Tachibana, T. Furuki, and S. Kanazawa Japanese Journal of Applied Physics 59, SHHE01 (2020) ○Development of local evacuation system for inhibiting oxidization in atmospheric-pressure plasma jet nitriding S. Chiba, R. Ichiki, T. Nakatani, T. Ueno, and S. Kanazawa Results in Physics 13, 102131 (2019) ○Peculiar Relationship of Plume Brightness and Hard Layer Formation in Atmospheric-Pressure Plasma Jet Nitriding R. Ichiki, T. Inoue, Y. Yoshimitsu, H. Yamamoto, S. Kanda, M. Yoshida, S. Akamine, and S. Kanazawa IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science 42, 2466 (2014) ○Steel nitriding by atmospheric-pressure plasma jet using N2/H2 mixture gas H. Nagamatsu, R. Ichiki, Y. Yasumatsu, T. Inoue, M. Yoshida, S. Akamine, and S. Kanazawa Surface and Coatings Technology 225, 26 (2013) ○Nitriding of steel surface by spraying pulsed-arc plasma jet under atmospheric pressure R. Ichiki, H. Nagamatsu, Y. Yasumatsu, T. Iwao, S. Akamine, and S. Kanazawa Materials Letters 71, 134 (2012) Nitro-Quenching with Atmospheric-Pressure Plasma JetNitro-quenching is a new heat treatment for steels using nitrogen instead of carbon. Its
low treatment temperature provides small thermal strains. We introduced
atmospheric-pressure plasma technology to nitro-quenching first to create
easy-to-use treatment.
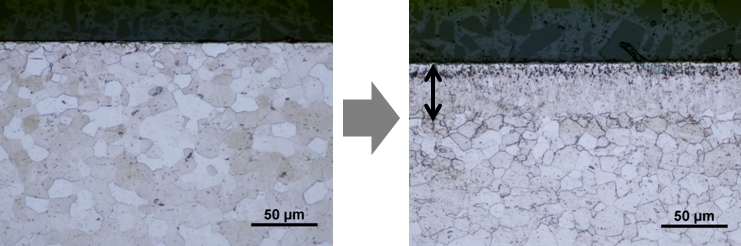 Formation of iron-nitrogen martensite layer on steel surface ○Controlling Nitrogen Dose Amount in Atmospheric-Pressure Plasma Jet Nitriding R. Ichiki, M. Kono, Y. Kanbara, T. Okada, T. Onomoto, K. Tachibana, T. Furuki, and S. Kanazawa Metals 9, 714 (2019) ○Experimental Demonstration of Nitro-Quenching by Atmospheric-Pressure Plasma Jet [in Japanese] T. Inoue, R. Ichiki, M. Mitani, M. Yoshida, S. Akamine, and S. Kanazawa Netsu-Shori (Heat Treatment) 55, 165 (2015) in Japanese Expanded Austenite Phase Formation on Stainless SteelsExpanded austenite phase is a nitrided, hard layer formed on the surface of austenite stainless
steels. We have achieved the formation of the surface layer by using the
hydrogen reduction to remove the passive layer.
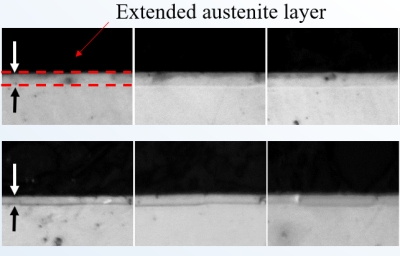 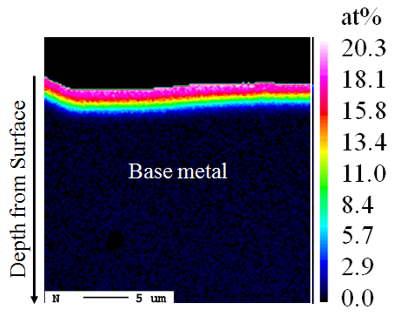 Formation of iron-nitrogen martensite layer on steel surface ○Reduction-Phase-Time Dependence of Atmospheric-Pressure-Plasma Nitriding for Stainless Steel R. Otani, R. Ichiki, K. Nakahara, H. Nishiguchi, K. Tachibana, T. Furuki, S. Kanazawa Abstract of 12th Asian-European International Conference on Plasma Surface Engineering, S4-PO13 (2019) ○Investigation on local formation of expanded austenite phase by atmospheric-pressure plasma jet A. Maeda, R. Ichiki, R. Tomizuka, H. Nishiguchi, T. Onomoto, S. Akamine, and S. Kanazawa Proceedings of the XXXIII International Conference on Phenomena in Ionized Gases, 169 (2017) Synthesis of Nitride Surfaces on Titanium
We can synthesis titanium nitride on titanium surface with the atmospheric-pressure
plasma jet. We expect easy treatment of titanium alloys as an biomedical material. The research on upgrading biocompatibility of titanium alloy is in progress.
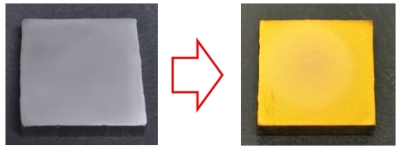 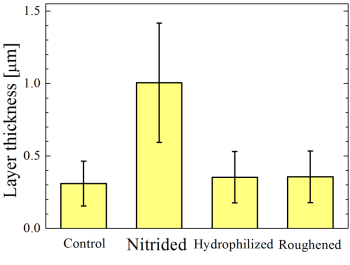 Formation of TiN surface with golden color and the thickness of the calcium phosphate layer on the samples ○Investigation on Hard-Tissue Compatibility of TiN Surface Formed by Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Nitriding R. Sannomiya, R. Ichiki, R. Otani, K. Hanada, M. Sonoda, S. Akamine, and S. Kanazawa Plasma and Fusion Research 13, 1306120 (2018) ○Atmospheric-pressure-plasma nitriding of titanium alloy Y. Yoshimitsu, R. Ichiki, K. Kasamura, M. Yoshida, S. Akamine, and S. Kanazawa Japanese Journal of Applied Physics 54, 030302 (2015) Nitriding using Dielectric Barrier Discharges (DBD)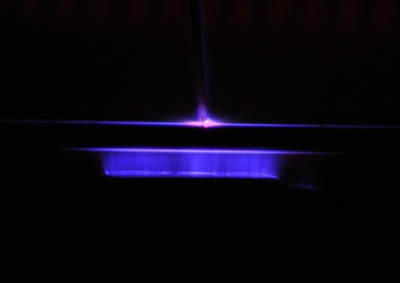 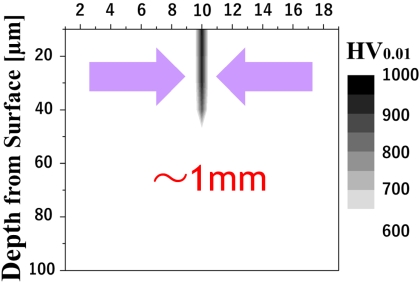 Photograph of DBD nitriding and cross-sectional hardness profile of locally treated sample ○Maskless Control of Local-Nitriding Area with Atmospheric-Pressure Barrier Discharge [in Japanese] K. Yakushiji, S. Wakabayashi, M. Ueda, Y. Shirai, R. Ichiki, K. Tachibana, T. Furuki, S. Kanazawa, and S. Yoshimura Netsu-Shori (Heat Treatment) 63, 205 (2023) in Japanese ○Simple Local Nitriding by Applying Non-Vacuum Plasma Technology R. Ichiki Movie in Japan Science and Technology Agency Meeting (2019) in Japanese ○Ignition-Area Extension of Dielectric Barrier Discharge under High Temperature R. Ichiki, T. Komatsu, K. Yakushiji, K. Tachibana, T. Furuki, S. Kanazawa, and S. Yoshimura Results in Physics 29, 104791 (2021) ○Investigation on Extended Phenomenon of DBD under High Temperature and Demonstration of Large-area Nitriding N. Kanda, R. Ichiki, K. Kawanobe, K. Tachibana, T. Furuki, S. Kanazawa Abstract of 12th Asian-European International Conference on Plasma Surface Engineering, S4-PO11 (2019) ○Demonstration of Nitriding by Dielectric Barrier Discharge and Investigation of Treatment Range Controllability K. Kitamura, R. Ichiki, T. Tsuru, S. Akamine, and S. Kanazawa Proceedings of 21st International Conference on Gas Discharges and their Applications, Vol. 2, 429 (2016)  Updated in 19 Apr 2023
Copyright (C) 2014- Oita University Kanazawa-Ichiki Lab. All Rights Reserved. |

