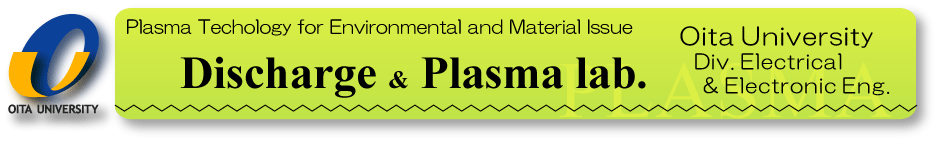
Our new concept is to irradiate discharge plasmas to a water film falling
on the internal wall of a pipe. This method enables high-speed, mass water
treatment. A 3D printer is utilized to create optimal reactor shapes. Recent
study has revealed that reactors providing swirl flows of dropping water
show high treatment efficiency.
○3D-Printed Atmospheric-Pressure Plasma Reactors
S. Kanazawa, K. Eto, W. Imagawa, S. Akamine, and R. Ichiki
International Journal of Plasma Environmental Science & Technology
9, 103 (2015)
PDF file
○Effect of Swirling Liquid Flow on Plasma-Based Water Treatment [in Japanese]
S. Matsunari, S. Akagawa, S. Akamine, R. Ichiki, and S. Kanazawa
The Institute of Electrostatics Japan (2015)
PDF file
○Preparation of Discharge-induced Plasma Reactor using a 3D Printer and
its Evaluation [in Japanese]
K. Eto, K. Fujisawa, S. Akamine, R. Ichiki, and S. Kanazawa
The Institute of Electrostatics Japan (2015)
PDF file
○Improvement of Surfactant Decomposition by Superposition of Pulsed Discharge on the Water and Ozone Injection
S. Kanazawa, S. Geng, T. Okawa, S. Akamine, and R. Ichiki
International Journal of Plasma Environmental Science & Technology
7, 21 (2013)
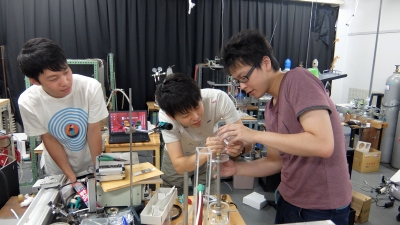
As an advanced oxidation processes, we are trying to realize the synergy effect of underwater streamers and
microbubbles.
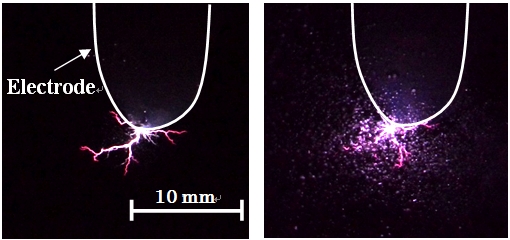
Photos of underwater streamers with and without microbubbles
○Characteristics of underwater discharge with microbubble [in Japanese]
Y. Anan, S. Akamine, R. Ichiki, and S. Kanazawa
The Annual Meeting of Japan Ozone Association (2015)
PDF file
○Discharge Characteristics in Water with Microbubbles [in Japanese]
Y. Anan, M. Kai, S. Yanagita, S. Akamine, R. Ichiki, and S. Kanazawa
The Japan Society of Applied Physics. Kyushu Branch (2014)
PDF file